13.02.24 - Reforestation as a solution to the ecologic crisis
This blog post gives little insights about the benefits of reforestation referring to different environmental aspects.

We at Pachamama Revive are focusing on reforestation on land and in cities. So, we want to share some reasons why reforestation will be a big part of the solution to save the planet.
And I don’t want to talk about problems a lot but just shortly. It’s a fact that climate change speeds up because of widespread deforestation; our soil degrades, and our water stays polluted because of a lack of trees and thus natural water filters. Just to mention a little part of it.
So let’s focus on the solutions and on reasons why we need to reforest and what positive impacts it has in the world.
1. Benefits for our sacred water!
Reforestation reduces Water Pollution: Acting as natural filters, forests help reduce pollution in rivers and streams, contributing to overall water cleanliness.
Reforestation for a balanced water cycle: Forests prevent extremes like floods and droughts, contributing to a balanced water cycle.
Reforestation helps regulate rainfall patterns: Forests contribute to the regulation of rainfall patterns, ensuring a consistent and sustainable water supply.
Reforestation preserves Aquatic Ecosystems: It safeguards aquatic habitats, supporting the survival of diverse marine and freshwater species.
Reforestation restores Watershed Health: Trees play a crucial role in maintaining watershed health, ensuring a sustainable supply of clean water for both human and natural communities.
Reforestation prevents Soil Erosion: Tree roots help stabilize soil, preventing erosion and sedimentation in water bodies. Reforestation acts as a natural barrier against soil runoff, preserving water quality downstream.
Reforestation mitigates Climate-Induced Water Challenges: Forests support resilience to climate change by maintaining consistent water flows, especially in regions prone to water scarcity.
Reforestation promotes Groundwater Recharge: Trees enhance groundwater recharge, replenishing underground aquifers.
Reforestation strengthens Biodiversity in Water Ecosystems: Forests foster biodiversity in water ecosystems, providing habitats for a variety of aquatic plants and animals.
Reforestation helps protect Drinking Water Sources: Reforestation ensures the sources of drinking water and the availability of clean and safe water for communities.

Benefits for our sacred water
Reforestation reduces Water Pollution: Acting as natural filters, forests help reduce pollution in rivers and streams, contributing to overall water cleanliness.
Reforestation for a balanced water cycle: Forests prevent extremes like floods and droughts, contributing to a balanced water cycle.
Reforestation helps regulate rainfall patterns: Forests contribute to the regulation of rainfall patterns, ensuring a consistent and sustainable water supply.
Reforestation preserves Aquatic Ecosystems: It safeguards aquatic habitats, supporting the survival of diverse marine and freshwater species.
Reforestation restores Watershed Health: Trees play a crucial role in maintaining watershed health, ensuring a sustainable supply of clean water for both human and natural communities.
Reforestation prevents Soil Erosion: Tree roots help stabilize soil, preventing erosion and sedimentation in water bodies. Reforestation acts as a natural barrier against soil runoff, preserving water quality downstream.
Reforestation mitigates Climate-Induced Water Challenges: Forests support resilience to climate change by maintaining consistent water flows, especially in regions prone to water scarcity.
Reforestation promotes Groundwater Recharge: Trees enhance groundwater recharge, replenishing underground aquifers.
Reforestation strengthens Biodiversity in Water Ecosystems: Forests foster biodiversity in water ecosystems, providing habitats for a variety of aquatic plants and animals.
Reforestation helps protect Drinking Water Sources: Reforestation ensures the sources of drinking water and the availability of clean and safe water for communities.

Benefits for our soil, our madre tierra!
Soil is the basis of life, essential for our existence; our food comes from it, and when we die, our bodies return to the soil. Did you know that approximately 1 billion microorganisms live in one kilogram of soil?However, healthy soil is crucial for a healthy planet. Reforesting automatically restores the soil. Trees can only thrive in healthy soil, and, conversely, trees help to restore the soil.
Here some general impacts that reforestation has on soil:
Conservation of Soil: Reforestation acts as a guardian, preserving our precious soil.
Stabilizing Roots: Tree roots stabilize the soil and prevent erosion.
Nutrient Cycles and Agriculture: Forests, integral to maintaining nutrient cycles, support agricultural productivity, ensuring fertile land for crops.
CO2 Sequestration: Healthy forest soil serves as a significant carbon sink, contributing to the mitigation of climate change.
Preventing Landslides:R eforestation serves as a natural barrier, preventing landslides and ensuring the stability of landscapes.
Feeding the World: Healthy soil is essential for feeding the world.

Benefits for our Air!
Air Purification by Trees: Trees act as natural air filters. Trees absorb pollutants, contributing to clean air.
Oxygen Production: During the process of photosynthesis, trees produce oxygen, aiding in maintaining the natural balance in the atmosphere.
Climate Regulation: Forests play a crucial role in regulating temperatures and climate conditions, supporting healthy air circulation.
CO2 Sequestration: Reforestation helps absorb and store carbon dioxide in trees, reducing greenhouse gas levels in the atmosphere.
Prevention of Air Pollution: Trees serve as a barrier against air pollution, filtering particles from the air and improving the quality of breathable air.

Benefits for biodiversity!
In response to the biodiversity crises, reforestation is a potent ally. By restoring diverse habitats, it actively promotes biodiversity. Here's how:
Habitat Restoration: Reforestation plays a crucial role in revitalizing habitats, providing a haven for a diverse range of plant and animal species.
Species Diversity: Diverse forests foster a rich tapestry of life. Reforestation focuses on reintroducing native species, ensuring a balanced and varied ecosystem.
Ecosystem Interconnectedness: Trees form complex ecosystems where various species depend on each other. Reforestation rebuilds these networks, securing the survival of interconnected species.
Protection of Endangered Species: Endangered species find support in reforested areas, as they recreate natural habitats essential for their survival.
Wildlife Corridors: Reforestation strategically creates wildlife corridors, facilitating safe movement between habitats and preventing isolation, thus promoting genetic diversity.
Pollinator Support: Trees attract diverse pollinators, contributing to the revival of crucial pollinator populations like bees and butterflies.
Microbial Diversity: Healthy soils, nurtured through reforestation, host a multitude of microorganisms vital for nutrient cycling and overall ecosystem health.

Benefits for our climate
Carbon Sequestration:
Trees and soil unite as Earth's natural carbon sink. During photosynthesis, they absorb carbon dioxide, actively mitigating climate change by reducing greenhouse gas concentrations.
Climate Regulation:
Forests play a vital role in regulating local and global climates. They influence temperature, humidity, and precipitation patterns. The transpiration process, where trees release water vapor, contributes to cloud formation and influences regional climate conditions.
Adaptation to Climate Change:
Diverse and resilient forests are essential for ecosystems to adapt to changing environmental conditions, especially those resulting from climate change. They act as natural buffer zones against extreme weather events and provide a shield against natural disasters.

Still questioning the value of reforestation? Here some benefits that reforestation has on society and economy
Job Creation and Economic Growth: Beside planting trees reforestation projects are about planting seeds of opportunity. By restoring forests, we create employment opportunities and stimulate local economies. From forestry jobs to ecotourism ventures, reforestation breathes life into communities.
Resource Abundance: Healthy forests are treasure troves of resources that sustain human well-being. Timber is just the beginning; forests also yield non-timber products and invaluable ecosystem services. These resources support industries, enhance livelihoods, and contribute to local economies.
Ecosystem Services: Ever heard of ecosystem services? Think of them as nature's gifts that keep on giving. Forests provide clean air, regulate climate, and purify water—essential services for our survival. Moreover, spending time in green spaces boosts mental health and reduces stress, offering a natural remedy in our fast-paced lives.
Cultural and Spiritual Enrichment: Forests are more than just trees; they're repositories of culture and heritage. Many indigenous communities depend on forests for their cultural identity and traditional practices. By restoring forests, we honor these traditions and preserve invaluable knowledge for future
29.11.2023 On the Path of Sustainability
The Transformative Power of Permaculture (1/2)
Pachamama Revive is guided by the life philosophy and principles of permaculture, aiming to integrate sustainable lifestyles into various fields. In this initial blog post on permaculture, we delve into questions such as:
What is permaculture, what ethics and principles does it follow, and how do we at Pachamama Revive harness the power of permaculture?
1. What is Permaculture?
The term and concept of permaculture originated in the 1970s in Australia, coined by Bill Mollison and David Holmgren, combining the words "permanent" and "agriculture."
Though initially conceived as a sustainable farming idea, permaculture has evolved into a holistic life philosophy that draws inspiration from nature. It identifies and utilizes patterns and principles from ecological contexts.
Permaculture is not a rigid method but a dynamic design process aimed at creating a sustainable world. This involves observing, analyzing, evaluating, implementing, and, through continuous observation, evolving and adapting concepts. The result is self-sustaining systems, including ecosystems capable of self-regeneration.
The application of permaculture is diverse, spanning from agriculture, daily life and education, to finance, and politics. A holistic approach is always pursued to create resource-efficient, life-sustaining cultures.
2. What Ethics Does Permaculture Follow?
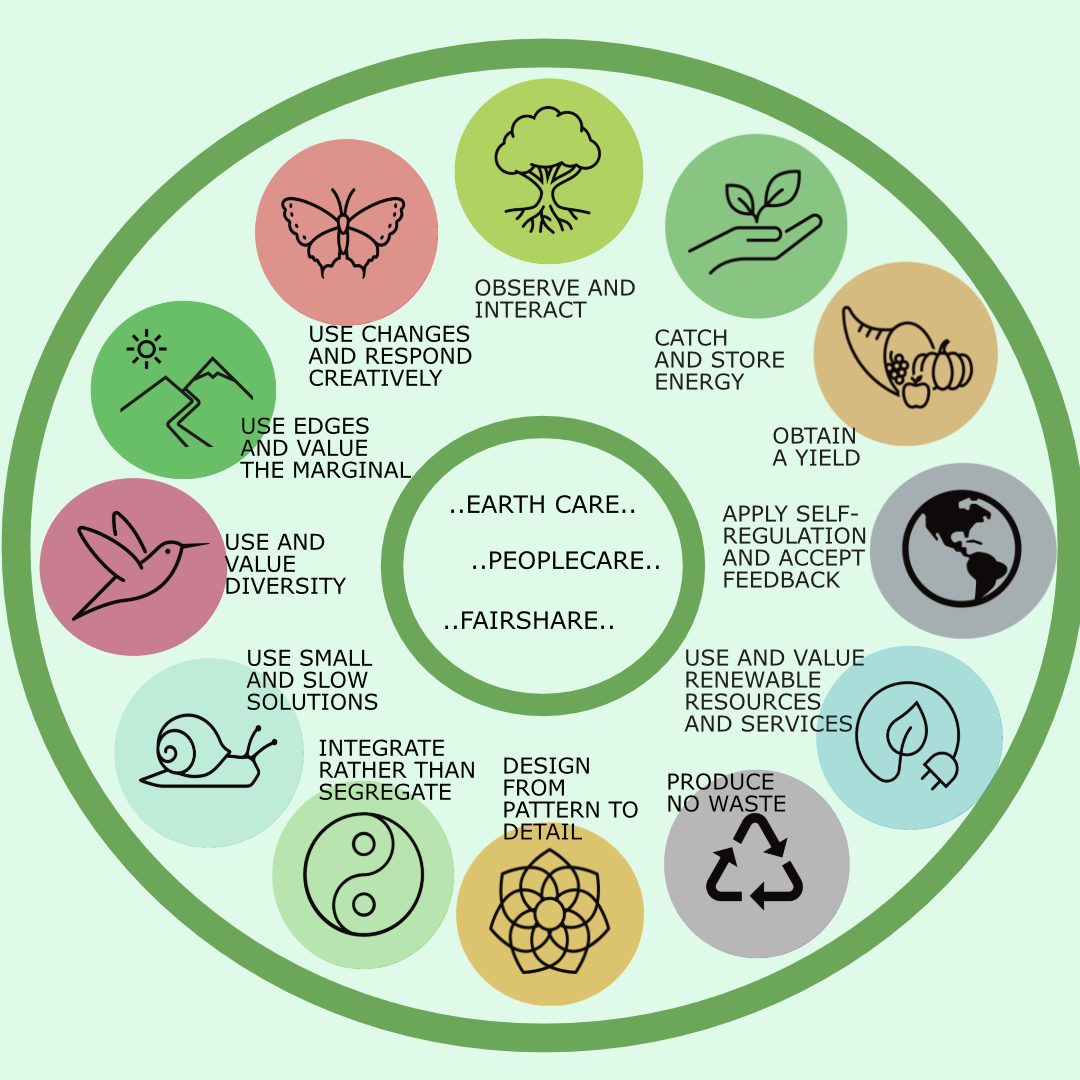
The ethical foundations of permaculture design practice are:
Earth Care
People Care
Fair Share - Limit Consumption and Growth; Share Surpluses
These three principles form the core of every permacultural project and are fundamental to creating a livable future. Besides agriculture, they extend to communities, individual lifestyles, education, health, economics, and politics.
3. What Principles Does Permaculture Follow?
Beyond ethical foundations, permaculture adheres to various principles for project design and daily life. The most well-known set of principles was developed by David Holmgren in his book "Permaculture: Principles and Pathways Beyond Sustainability." These principles succinctly capture the features of resilient and sustainable systems.
Their formulation is based on extensive observation of ecological connections, the exploration of sustainable cultural practices, personal experience in gardening and land management, and the application of systems thinking. The principles serve to cultivate an alternative mindset and make decisions that are sustainable for future generations.
The permaculture design principles are:
- Observe and Interact
- Catch and Store Energy
- Obtain a Yield
- Apply Self-Regulation and Accept Feedback
- Use and Value Renewable Resources and Services
- Produce No Waste
- Design from Patterns to Details
- Integrate Rather Than Segregate
- Use Small and Slow Solutions
- Use and Value Diversity
- Use Edges and Value the Marginal
- Use Change and Respond Creatively to It
I am personally a big fan of these principles, as they come from the observation of functioning, healthy ecosystems and are applicable to various areas, including individual lives. They embody profound wisdom and, when implemented, can contribute to increased efficiency, effectiveness, energy, health, balance, justice, and love, both for individuals and the external world.
Pachamama Revive and the Transformative Power of Permaculture
Pachamama Revive aligns with both the ethics and principles of permaculture. Our goal is to cultivate a deep understanding that humans are part of nature and that together, in community, we can create a sustainable future.
We use the transformative power of permaculture to guide thinking toward nature-based solutions, applying and evolving them. We encourage each individual to work with nature, both their inner nature and the external environment.
May this article contribute to raise awareness about the profound significance of permaculture and inspire us all to find our own path on the journey of sustainability.
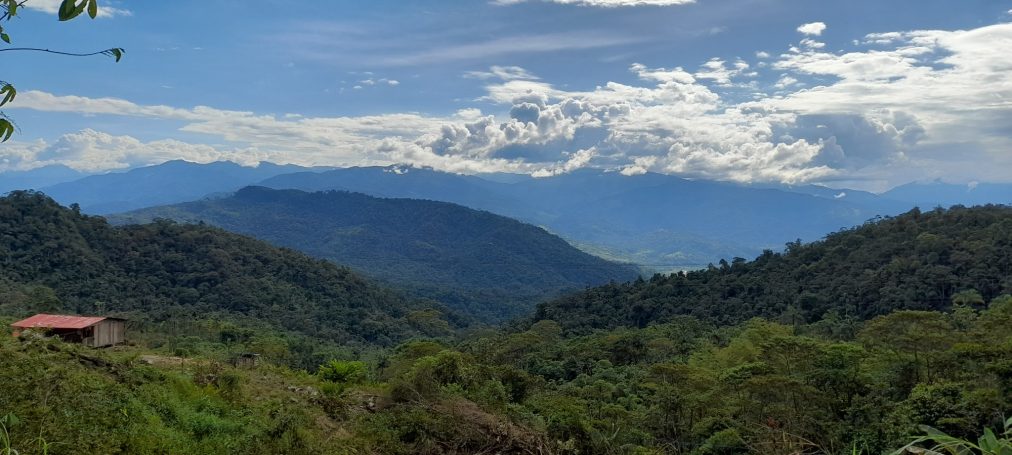
19.11.23 Putumayo, Colombia
A little journey through the region
In southern Colombia, a region that is both geographically and spiritually fascinating unfolds – Putumayo. For Pachamama Revive, this pearl of Colombia is more than just a location on the map - it is a vibrant mosaic of captivating nature, rich cultural diversity, and a profound spiritual heritage waiting to be discovered and protected.
Let me share more about Putumayo.
Putumayo is vibrant and diverse – yes, a pearl of Colombia –
My connection to this region is deeply rooted. The initial encounters during a journey in 2019 opened doors to a deeper awareness and a stronger connection to Mother Earth. Traditional medicine, shared in ceremonies with the locals, revealed to me the powerful effects of plants and the profound healing potential palpable in Putumayo.
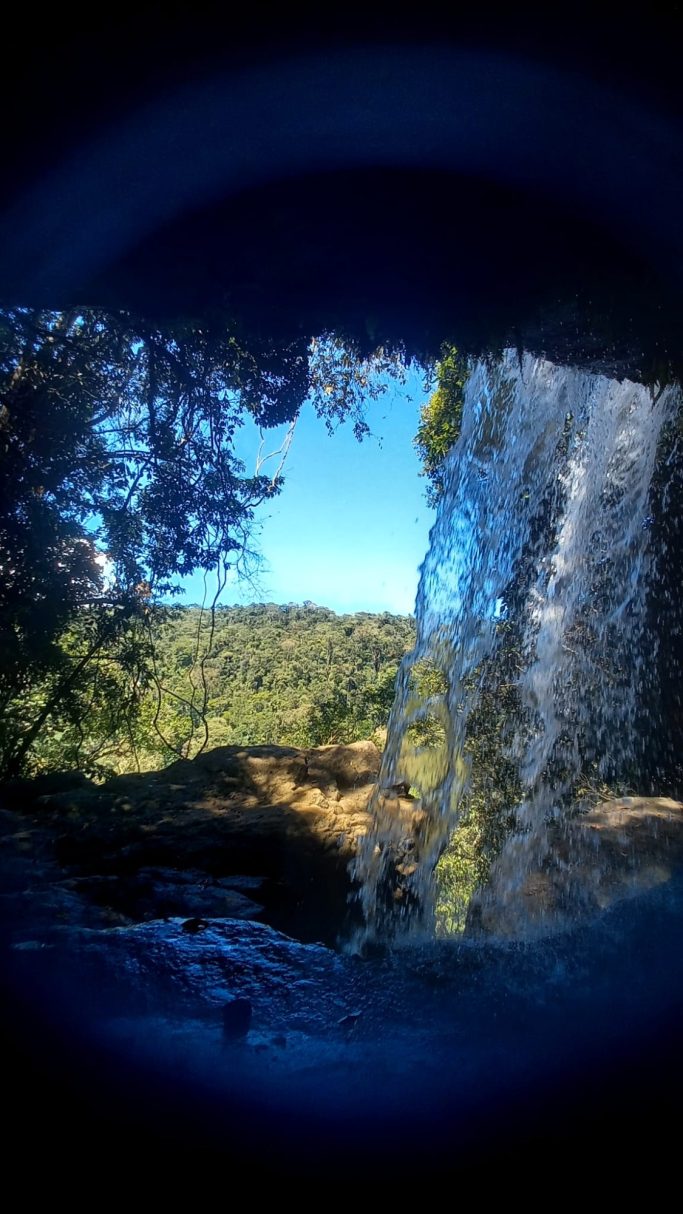
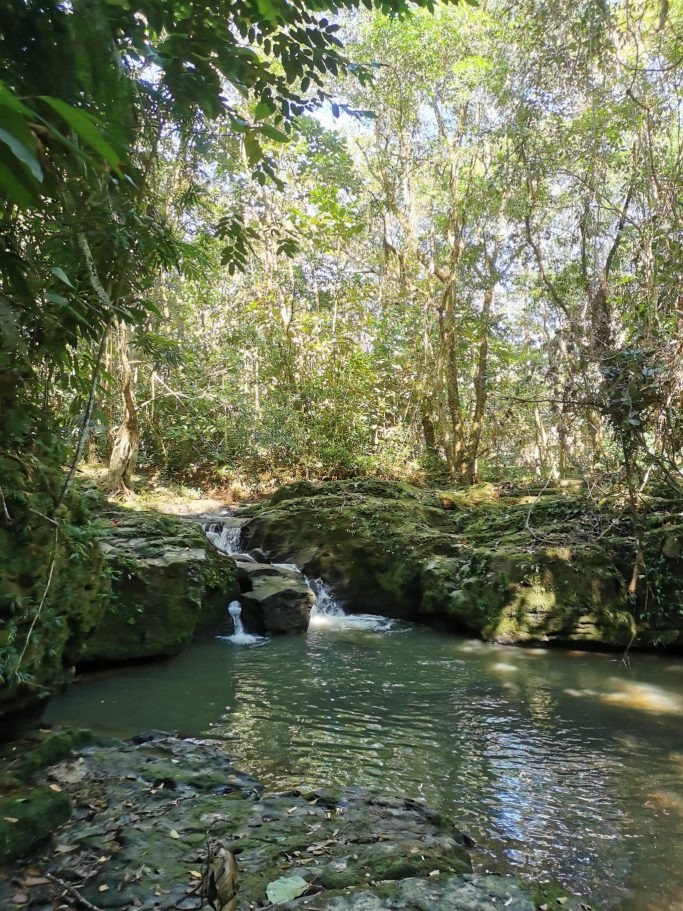
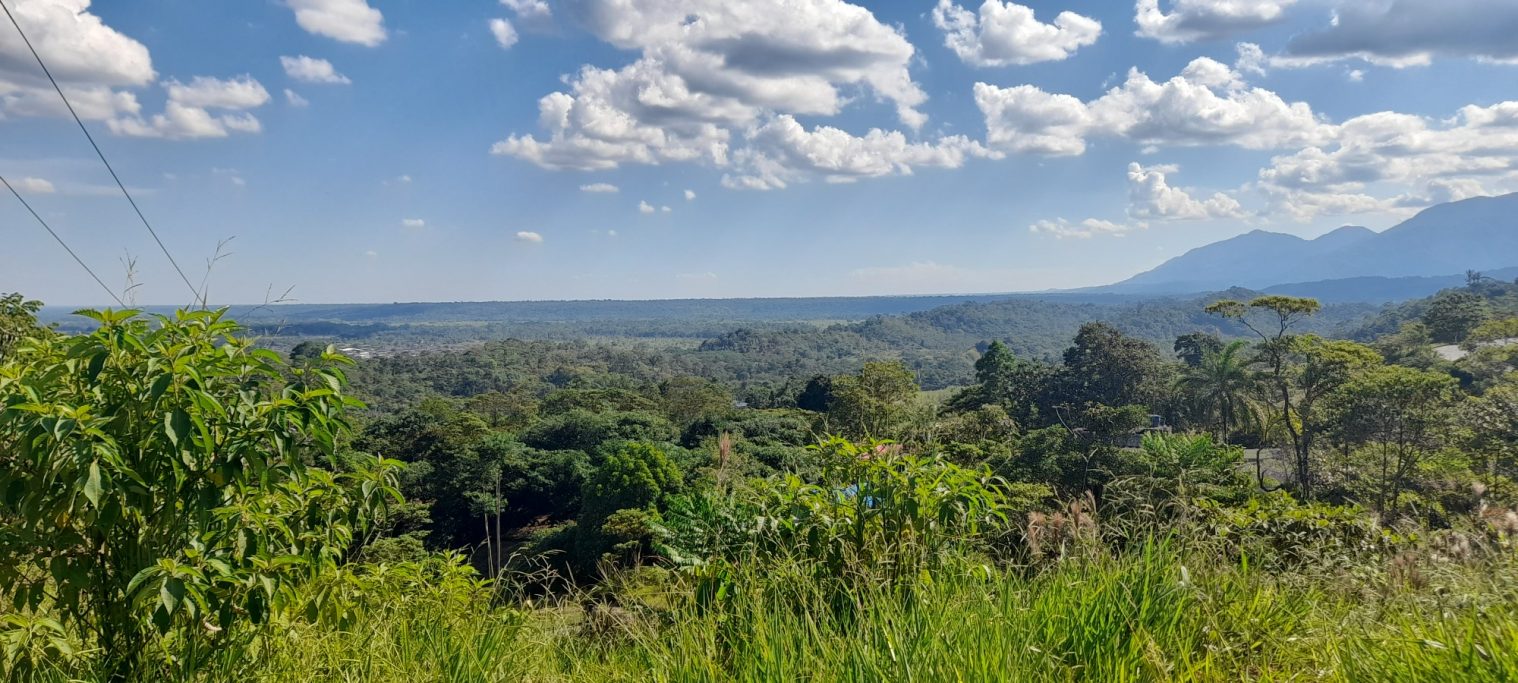
On the other side, Putumayo fascinates with breathtaking nature, a mega-diverse flora and fauna. It stretches in southern Colombia, nestled in the eastern Andes foothills and the beginning of the Amazon basin. From fog-covered páramo heights to wild waterfalls on the route from Sibundoy to Mocoa, where wild tapirs,andean bears, hummingbirds, and many other species reside.
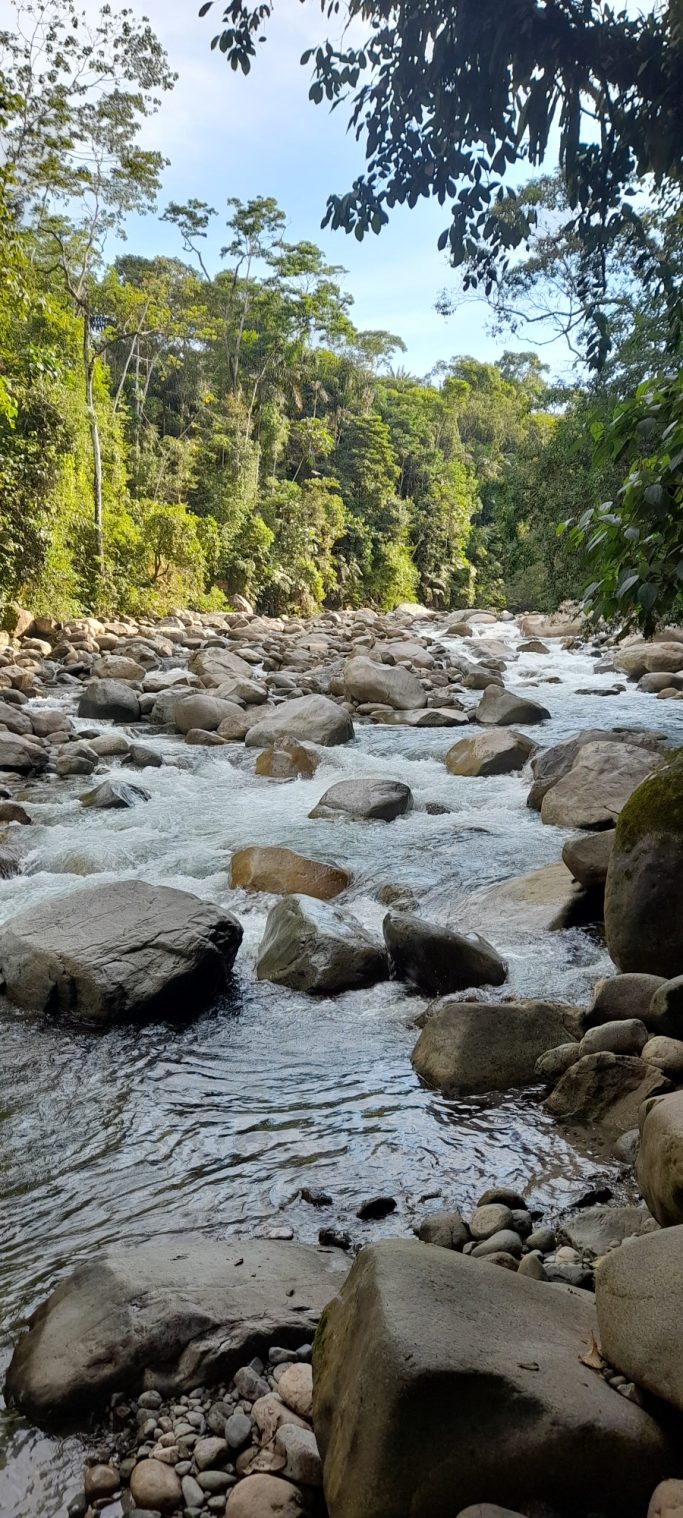
The tropical region around the capital Mocoa, situated at about 600 meters altitude, impresses with its unique landscape characterized by lush jungle and numerous waterfalls. Notable here is the Fin del Mundo waterfall at the mocoa river. The uniqueness of this environment lies, among other things, in its exceptional geology and the glittering stones found in the riverbed. When bathing in the rivers, the water sometimes appears in green shimmer, created by stones like aventurines. But there are also many other extraordinary rocks, crystals, and fossils that all harbor stories of the past.
Further east, the deeper Amazon region unfolds. The Caquetá and Putumayo rivers cross the area, surrounded by a rich flora and fauna, including jaguars, panthers, ocelots, snakes like the Boa Constrictor, the Anaconda, crocodiles, macaws, various turtle species, countless insects, and more.
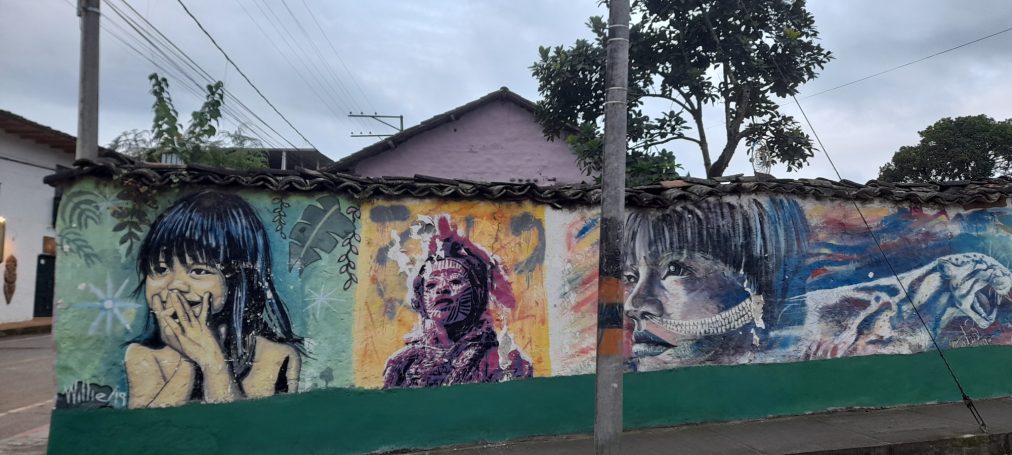
And the diversity of Putumayo is reflected not only in the stunning nature but also in the cultural diversity of the different indigenous tribes and languages. Communities like the Camentzä in Sibundoy not only preserve their traditional customs but also share their ancient knowledge of traditional medicine and rituals. The variety of languages spoken by indigenous groups like the Cofán, Inga, Huitoto, Siona, Secoya, or Shuar contributes to the unique cultural mix of this region. These indigenous communities are not only guardians of their history but also play a crucial role in maintaining ecological balance and the sustainable use of natural resources.
As impressive as the ecosystems and cultures in Putumayo are – like so many places on Earth, Putumayo is threatened by deforestation, mining, illegal logging, oil extraction, infrastructure projects, and overfishing. It requires cross-cutting projects that operate functional nature conservation and promote social issues.
Therefore, we at Pachamama Revive firmly root our intentions in the soil of Putumayo – in our first project near Mocoa in the Amazon region – we plan to protect and sustainably use land to maintain ecological balance, support local flora and fauna, establish eco-villages, build retreat centers, and realize sustainable projects in close collaboration with the indigenous population. We rely on sustainable cultivation methods and plan permaculture gardens based on the principles of syntropic agriculture.
We also commit to protecting the shrinking habitats of jaguars, tapirs, and other endangered species.
This short piece is more than just a report on the region. It is a declaration of love for the beauty and culture of Putumayo and the responsibility we bear to advocate for a greener, healthier planet.
If our mission resonates with you, join us on the journey and become part of Pachamama Revive!
Dive in, share your thoughts, and let us together raise awareness of the uniqueness of Putumayo.
Feel free to share this article and be part of the movement that Pachamama Revive has initiated.
Lots of love
A few more impressions
Keep up-dated and
sign-up for our newsletter!
©Copyright. All rights reserved.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte prüfen Sie die Details und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.













